Spark
RDD Programming
A Resilient Distributed Dataset (RDD), the basic abstraction in Spark. Represents an immutable, partitioned collection of elements that can be operated on in parallel.
简单而言,RDD 可以视作分布式环境下的数组,拥有高效、稳定的优点。RDD 通过内存计算、分区策略 (Partition) 与调度优化器 (Scheduler) 以实现高效的并行计算,RDD 不可变性特点便于实现部分缓存备份,容错性使其在分布式环境下具备稳定的优点。
Example
https://github.com/apache/spark/blob/master/examples/src/main/python/wordcount.py
# word count
lines = spark.read.text(sys.argv[1]).rdd.map(lambda r: r[0])
counts = lines.flatMap(lambda x: x.split(' ')) \
.map(lambda x: (x, 1)) \
.reduceByKey(add)
output = counts.collect()
for (word, count) in output:
print("%s: %i" % (word, count))
Representation
In a nutshell, we propose representing each RDD through a common interface that exposes five pieces of information: a set of partitions, which are atomic pieces of the dataset; a set of dependencies on parent RDDs; a function for computing the dataset based on its parents; and metadata about its partitioning scheme and data placement.1
RDD 由分区、依赖、计算函数、元数据构成,通过分区、依赖、计算函数构建 RDD 之间的计算图,元数据是各节点组成分布式系统的上下文信息。
Compute
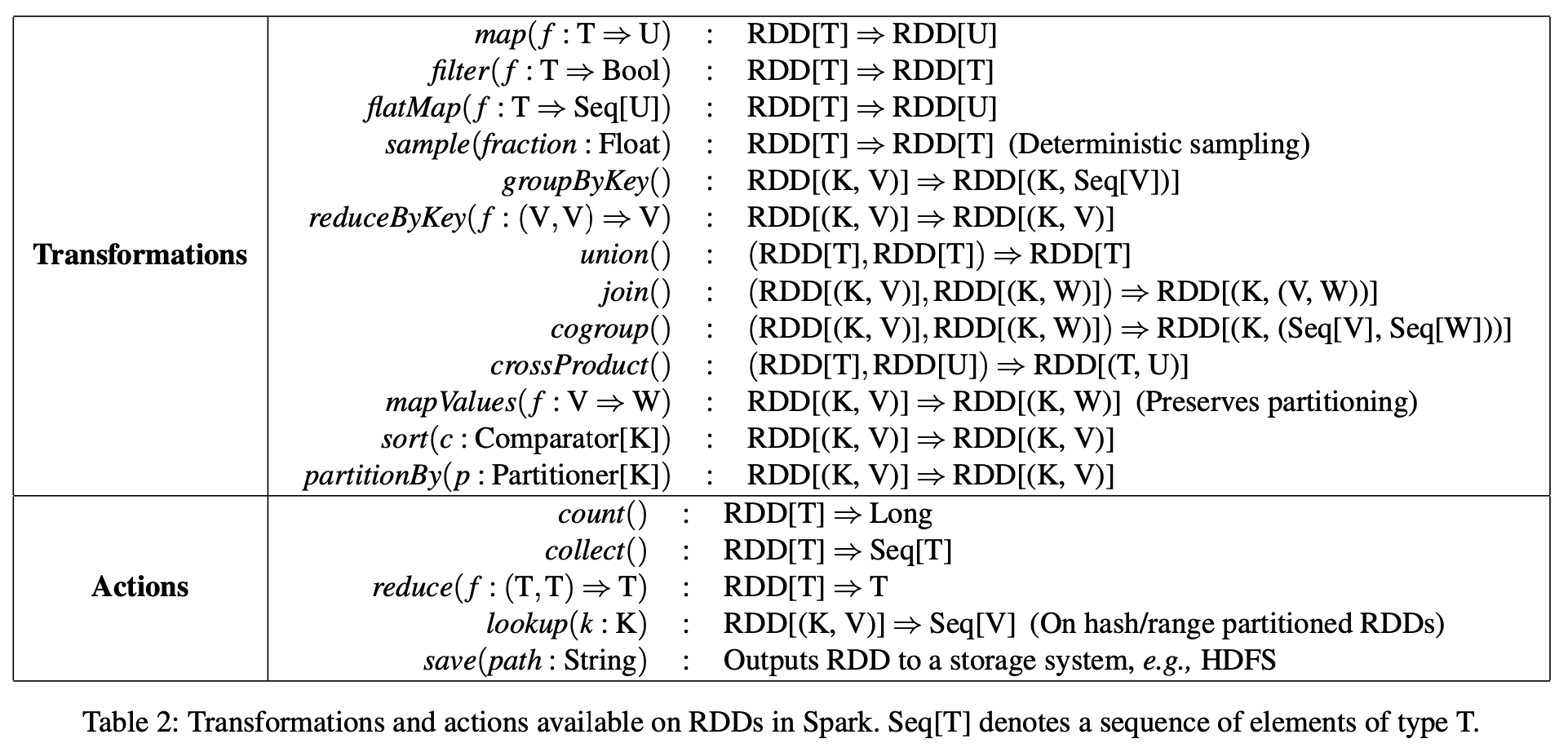
RDD 包括两类基本函数,一类为 Transformations (return a new RDD),另一类为 Actions (launch a job to return a value to the user program)。
Table 2: Transformations and actions available on RDDs in Spark. Seq[T] denotes a sequence of elements of type T.1
map是 Transformations 中的基本函数,按f函数功能描述实现 RDD 的转换。
def map[U: ClassTag](f: T => U): RDD[U] = withScope {
val cleanF = sc.clean(f)
new MapPartitionsRDD[U, T](this, (_, _, iter) => iter.map(cleanF))
}
colect是 Actions 中的函数之一,其功能是将 RDD 各分区元素收集至driver。由sc.runJob将计算任务提交并真正执行。
def collect(): Array[T] = withScope {
val results = sc.runJob(this, (iter: Iterator[T]) => iter.toArray)
Array.concat(results: _*)
}
Parallel
RDD 描述了数据的存在状态,通过 Transformations 算子实现状态之间的转换,构建数据的计算图。RDD 将数据划分为多个分区 (Partition),分区是进行独立并行计算的基本单位,并通过依赖 (Dependency) 描述分区之间的数据依赖关系。
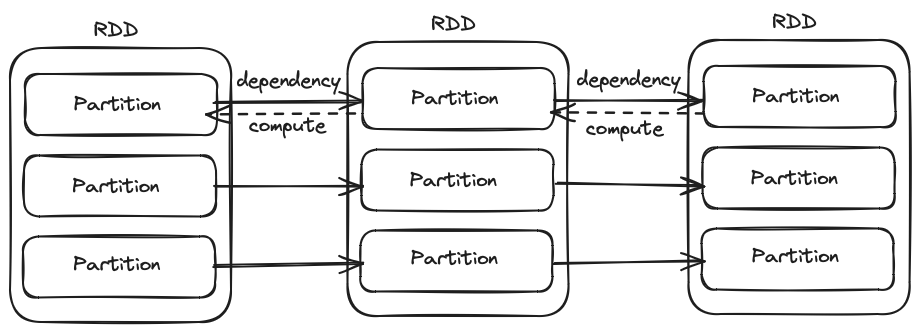
RDD 通过 getPartitions 与 getDependencies 方法描述如何获取分区与依赖,分区与依赖是构建 RDD 计算流的基础。
protected def getPartitions: Array[Partition]
protected def getDependencies: Seq[Dependency[_]] = deps
📌
getPartitions与getDependencies是子类需要重写的方法,外部调用 API 是partitions与dependencies。
RDD compute 方法是执行计算流的入口,split 参数描述了当前 RDD 需要计算的分区,context 是计算任务携带的上下文。compute 所构建的计算模式是根据 split 分区与 RDD 之间的依赖关系进行的反向计算。
def compute(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T]
Partition
To-Do
Dependency
We found it both sufficient and useful to classify dependencies into two types: narrow dependencies, where each partition of the parent RDD is used by at most one partistion of the child RDD, wide dependencies, where multiple child partitions may depend on it. For example, map leads to a narrow dependency, while join leads to to wide dependencies (unless the parents are hash-partitioned).1

依赖分为两类基本依赖,即 narrow dependencies 和 wide dependencies。
Distribution
RDD 之间构成的计算图,描述了数据之间的流转关系,分区为并行计算描述了数据的划分方式,依赖则指明分区之间存在的数据依赖关系。问题在于,Spark 如何基于 RDD 描述构建分布式计算?
📌 Spark 如何基于 RDD 描述构建分布式计算?
把需要进行大量计算的工程数据分割成小块,由多台计算机分别计算,再上传运算结果后,将结果统一合并得出数据结论的科学。
Wikipedia 对分布式计算的描述包括两小点,一是将计算数据分割成小块,二是将数据交由多台计算机分别计算与汇总过程,Parallel 小节说明了 RDD 分区划分概念,本节 Distribution 将说明 RDD 分区调度与计算的过程。
实际上,Spark 计算节点以 Task 为最小基本单位,按线程级别执行并行计算。RDD 所构成的计算图经过切分得到计算的最小基本单位 Task。
Whenever a user runs an action (e.g., count or save) on an RDD, the scheduler examines that RDD’s lineage graph to build a DAG of stages to execute, as illustrated in Figure 5. Each stage contains as many pipelined transformations with narrow dependencies as possible. The boundaries of the stages are the shuffle operations required for wide dependencies, or any already computed partitions that can short-circuit the computation of a parent RDD. The scheduler then launches tasks to compute missing partitions from each stage until it has computed the target RDD.1
Job-Stage-Task 示意图,

Job 是对由 RDD 构成的计算图进行计算的任务单位,Spark DAGScheduler 负责根据 Job 中的数据依赖关系,主要是 wide-dependency 划分为多个 Stage (wide-dependency 处下游 RDD 中的分区计算依赖于多个上游 RDD 的分区结果,即计算不可连续构成 Pipeline)。
Stage 包括两种类型 Stage,分别是 ResultStage 与 ShuffleMapStage,前者可以视作是 final Stage,即最后的输出结果的 RDD 及其 narrow-dependency 的 parents RDD 所构成的 Stage;后者即与 final Stage 之间存在 wide-dependency 的上游 Stage。经过 wide-dependency 划分后,ResultStage 与 ShuffleMapStage 内部只存在 narrow-dependency。
Task 是对由 Stage 内部依赖约束、相同分区所形成的计算链进行计算的任务单位,Task 是最小的任务单位,Task 经调度单元 (Scheduler) 转发至执行单元 (Executor),每个 Task 由单独的线程进行计算。
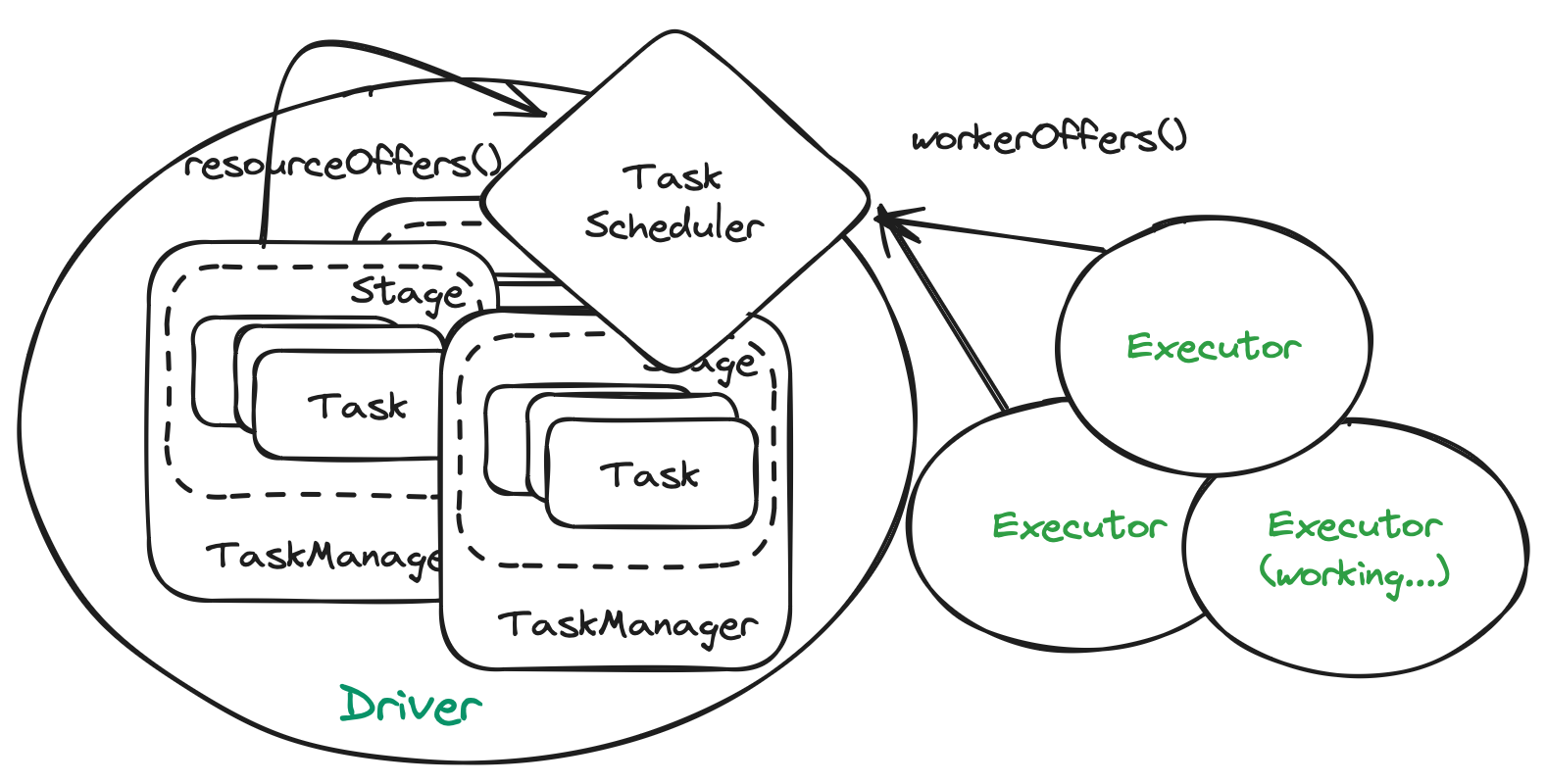
DAGScheduler 从 RDD 构成的计算图,经过 Job、Stage、Task 的细化拆分后,最后将需要进行计算的 Task 提交至 TaskScheduler,而后者将跟踪这些 Task 以及空闲的计算节点,按调度策略将 Task 分发至各计算节点,其中一种调度策略是,将空闲的节点先进行混淆,再依次分发待计算的任务到各节点。
Scheduler
To-Do
How Spark runs a Job?
To-Do
// getShuffleDependenciesAndResourceProfiles
while (waitingForVisit.nonEmpty) {
val toVisit = waitingForVisit.remove(0)
if (!visited(toVisit)) {
visited += toVisit
Option(toVisit.getResourceProfile()).foreach(resourceProfiles += _)
toVisit.dependencies.foreach {
case shuffleDep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _] =>
parents += shuffleDep
case dependency =>
waitingForVisit.prepend(dependency.rdd)
}
}
}