Algorithm
Two Sum
| Two Sum | HashMap |
|---|
Given an array of integers nums and an integer target, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
You can return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9 Output: [0,1] Explanation: Because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9, we return [0, 1].
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,2,4], target = 6 Output: [1,2]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [3,3], target = 6 Output: [0,1]
Constraints:
2 <= nums.length <= 104-109 <= nums[i] <= 109-109 <= target <= 109- Only one valid answer exists.
O(n2) time complexity?
Solution:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int> &nums, int target) {
unordered_map<int, int> num2index(0);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
auto it = num2index.find(target - nums[i]);
if (it == num2index.end()) {
num2index[nums[i]] = i;
continue;
}
return {it->second, i};
}
return {};
}
};
Add Two Numbers
| Add Two Numbers | LinkedList |
|---|
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example 1:
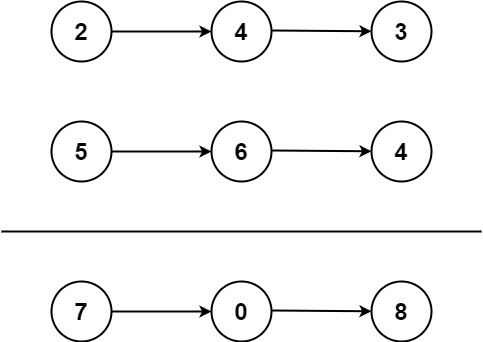
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] Output: [7,0,8] Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
Example 2:
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0] Output: [0]
Example 3:
Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9] Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
Solution:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *addTwoNumbers(ListNode *l1, ListNode *l2) {
ListNode dummy;
ListNode *p = &dummy;
ListNode *pl1 = l1;
ListNode *pl2 = l2;
auto tmp = 0;
auto add = [&tmp, &p](int sum) {
sum += tmp;
tmp = sum / 10;
p->next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
p = p->next;
};
while (pl1 != nullptr && pl2 != nullptr) {
add(pl1->val + pl2->val);
pl1 = pl1->next;
pl2 = pl2->next;
}
while (pl1 != nullptr) {
add(pl1->val);
pl1 = pl1->next;
}
while (pl2 != nullptr) {
add(pl2->val);
pl2 = pl2->next;
}
if (tmp > 0) {
add(0);
}
return dummy.next;
}
};
Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
| Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters | Sliding-Window |
|---|
Given a string s, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
Example 1:
Input: s = "abcabcbb" Output: 3 Explanation: The answer is "abc", with the length of 3.
Example 2:
Input: s = "bbbbb" Output: 1 Explanation: The answer is "b", with the length of 1.
Example 3:
Input: s = "pwwkew" Output: 3 Explanation: The answer is "wke", with the length of 3. Notice that the answer must be a substring, "pwke" is a subsequence and not a substring.
Constraints:
0 <= s.length <= 5 * 104sconsists of English letters, digits, symbols and spaces.
Solution:
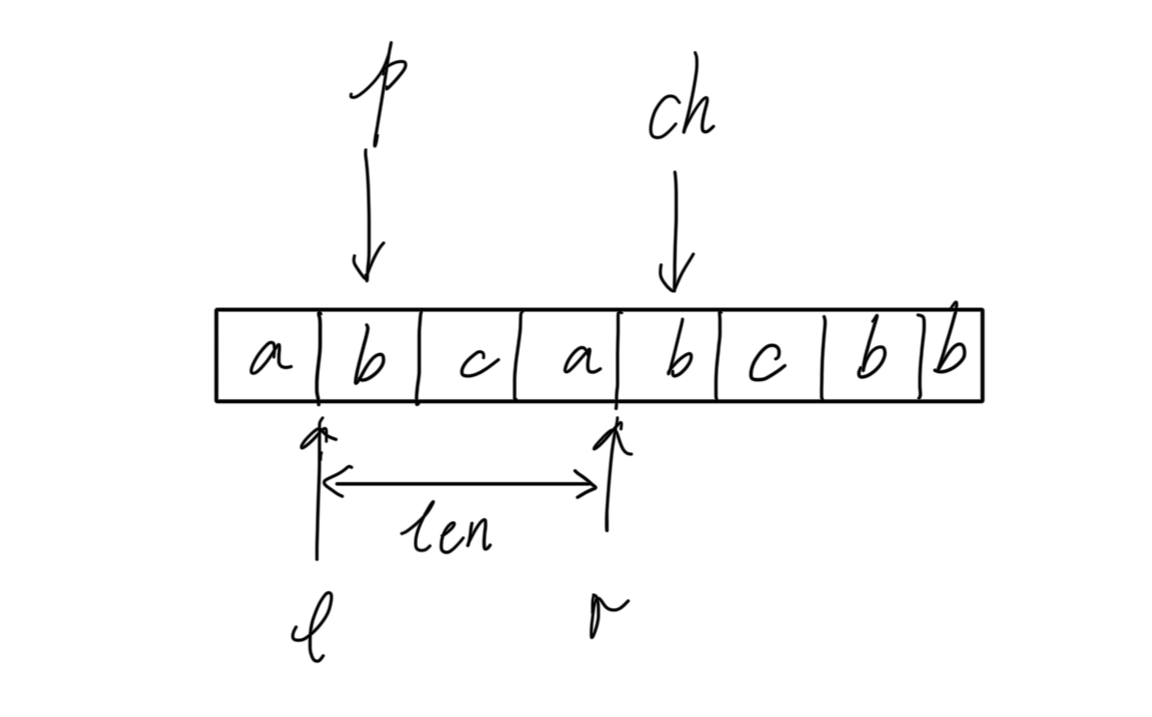
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int maxLength = 0;
int bitmap[256] = {};
int lhs = 0;
int rhs = 0;
for (char ch : s) {
if (bitmap[ch] == 1) {
int p = lhs;
while (s[p] != ch) {
bitmap[s[p]] = 0;
p++;
}
lhs = p + 1;
}
bitmap[ch] = 1;
rhs += 1;
if (rhs - lhs > maxLength) {
maxLength = rhs - lhs;
}
}
return maxLength;
}
};
Median of Two Sorted Arrays
| Median of Two Sorted Arrays | Binary Search |
|---|
Given two sorted arrays nums1 and nums2 of size m and n respectively, return the median of the two sorted arrays.
The overall run time complexity should be O(log (m+n)).
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [1,3], nums2 = [2] Output: 2.00000 Explanation: merged array = [1,2,3] and median is 2.
Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3,4] Output: 2.50000 Explanation: merged array = [1,2,3,4] and median is (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5.
Constraints:
nums1.length == mnums2.length == n0 <= m <= 10000 <= n <= 10001 <= m + n <= 2000-106 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 106
Solution: